¶ The principle of scanning code login
To summarize in one sentence: Scanning code login is essentially the process of the login requesting party requesting the logged-in party to write the login credentials into the specific medium. The login requesting party here is the Web end, the logged-in party is the APP end, the login credentials can be user information, or the credentials exchanged for user information, and the specific medium is a QR code.
The specific scanning code login process is as follows:
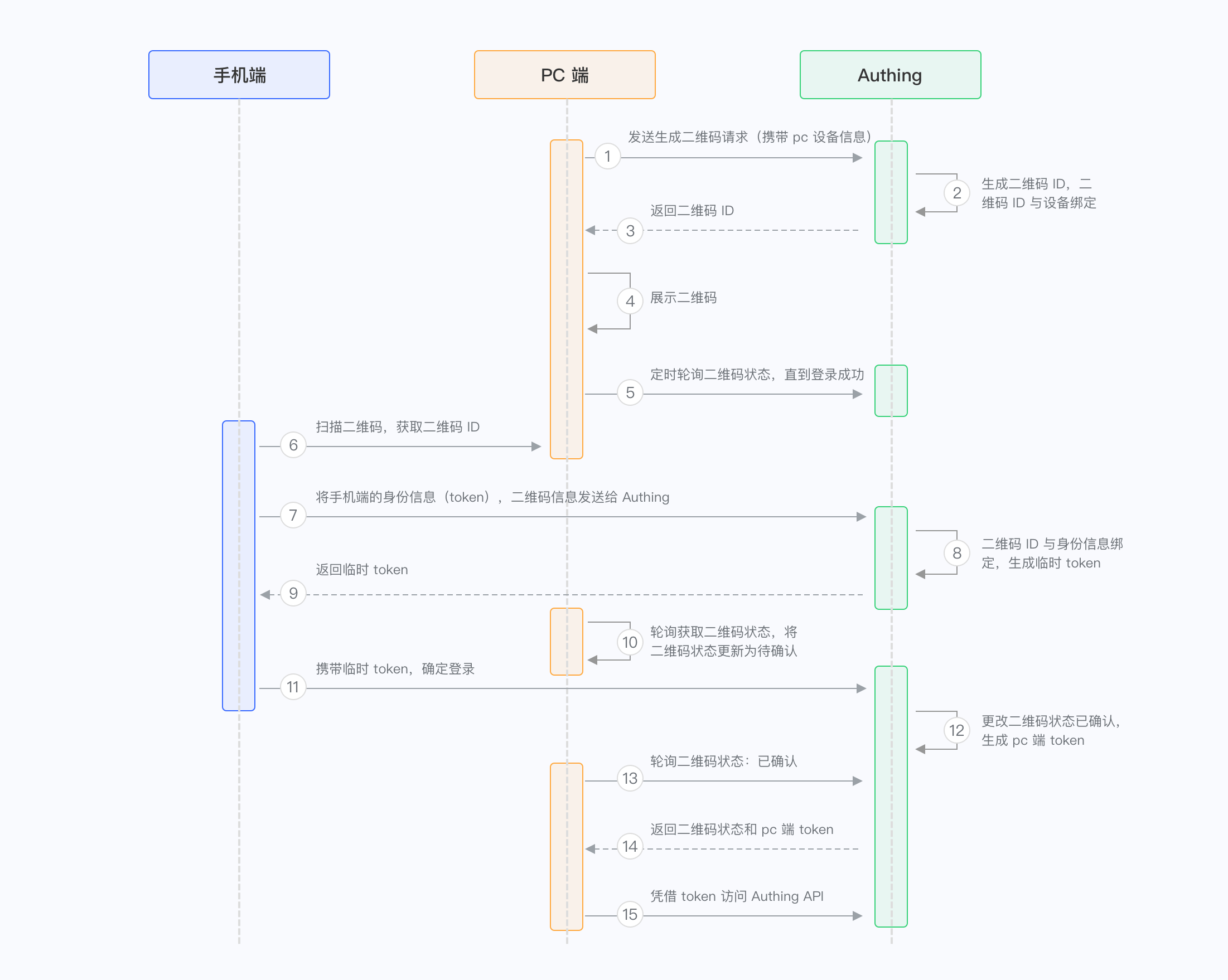
Open the login page, display a QR code, and poll the QR code status(web)
After opening the APP to scan the QR code, the APP displays the confirmation and cancel buttons(app)
The login page displays the scanned user's avatar and other information(web)
The user clicks to confirm the login on the APP(app)
The login page knows from the polling QR code status that the user has confirmed the login and obtains the login credentials(web)
The page login is successful and enters the main application page(web)
In the whole process, a specific QR code serves as a bridge connecting the party requesting login and the party that has logged in. The QR code is essentially a piece of text information converted into a picture that can be decoded and recognized through a certain agreed encoding method. Its essence is a piece of text information. Therefore, we can write information such as QR code ID, creation time, expiration time, etc. into the QR code. The APP terminal can recognize the QR code by decoding the QR code information (this is the basic function of the terminal medium). On the Web side, there is generally an interface for requesting the generation of a QR code. This interface will return the QR code ID and QR code connection. The ID is used to query the latest status of the QR code, and the link is used for display. In this way, the Web side and the APP side have established a consensus: QR code ID. The APP side modifies the QR code status through authorization, and the Web side can monitor the QR code status changes through polling and obtain the login credentials to complete the login. Let's break it down in detail. What are the states of the QR code:
- Not scanned
- Scanned, waiting for user confirmation
- Scanned, user agrees to authorization
- Scanned, user cancels authorization
- Expired
The APP can modify the state of the QR code, and a total of three interfaces will be used:
- Confirm that it has been scanned
- Agree to authorization
- Cancel authorization
Once the Web end monitors that the QR code state has changed to Agree to authorization, the login is complete. When the APP end requests these interfaces, it needs to bring the login credentials (this is obvious), and the backend interface can determine the user who agrees to the authorization, thereby binding the QR code ID and the user ID.
For more information, see:
- [**Scan code login practical series 1: Principle and process design**](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100026915)
- [**Scan code login practical series 2: Backend interface implementation**](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100027688)
- [**Scan code login practical series 3: Front-end SDK encapsulation**](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100027862)
- [**Scan code login practical series 4: Summary**](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100028054)
