¶ Become an OAuth 2.0 identity source
This article describes how to make GenAuth an OAuth2.0 identity source. Other systems can access GenAuth as an identity provider through the OAuth2.0 protocol.
The OAuth2.0 protocol has the following authorization modes: Authorization code mode, Implicit mode, Password mode. After becoming an OAuth2.0 identity source, other applications can use the corresponding mode process to complete user authentication and authorization.
You can learn more about the OAuth 2.0 protocol here.
¶ Create an application
In order to enable your application to have identity authentication capabilities, you need to create an application in GenAuth. It is recommended to fill in the name of your actual application project. Go to Console > Application > Application List and click Create Application:
Fill in your Application Name, for example: Network Notes Project, and specify an Authentication Address for your project, where your users will complete authentication in the future. Callback Link Fill in your project Backend Route, where GenAuth will send user information (to be exact, an authorization code) to this address. Finally, click Create.
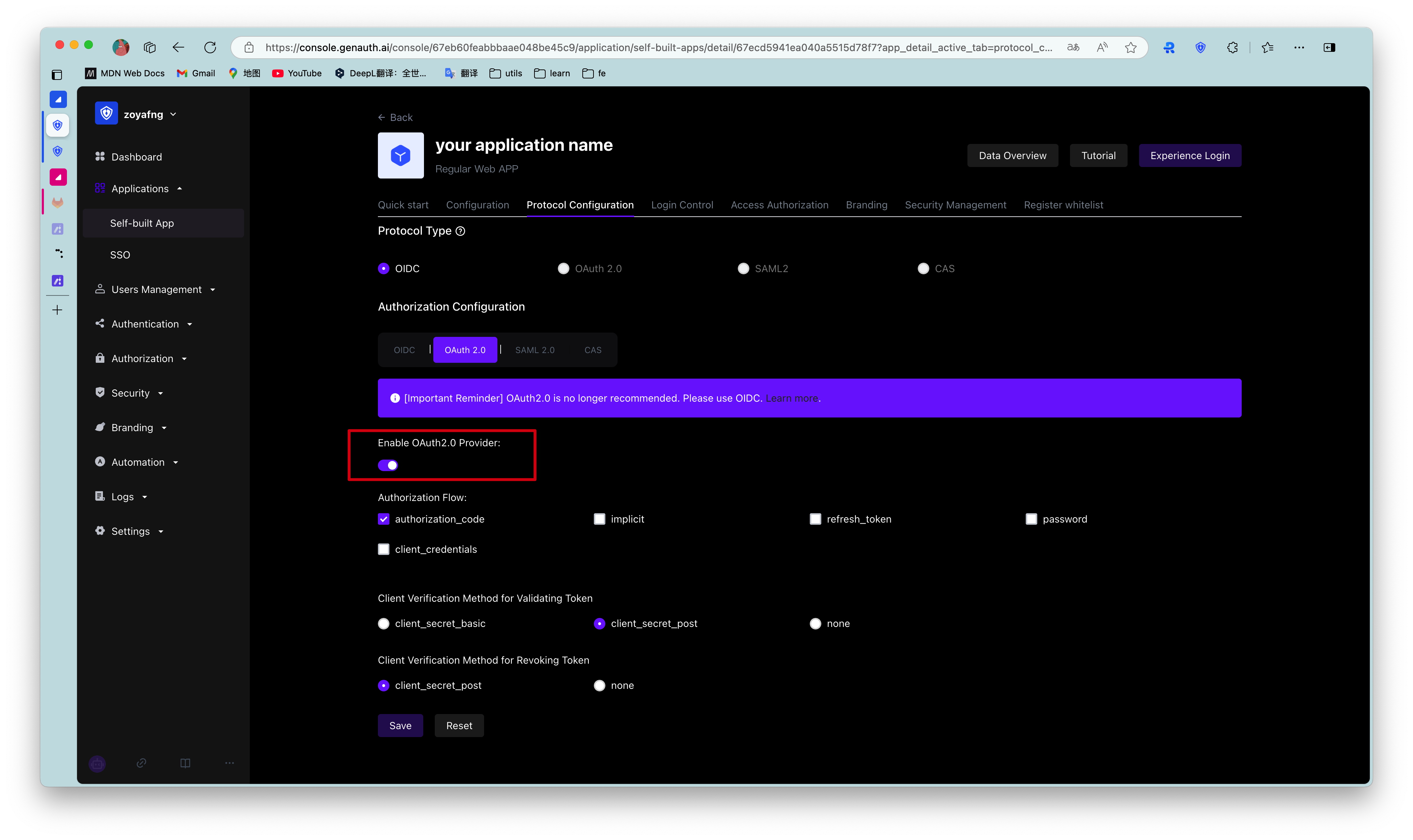
Find your application and go to the "Enable Identity Provider" tab.
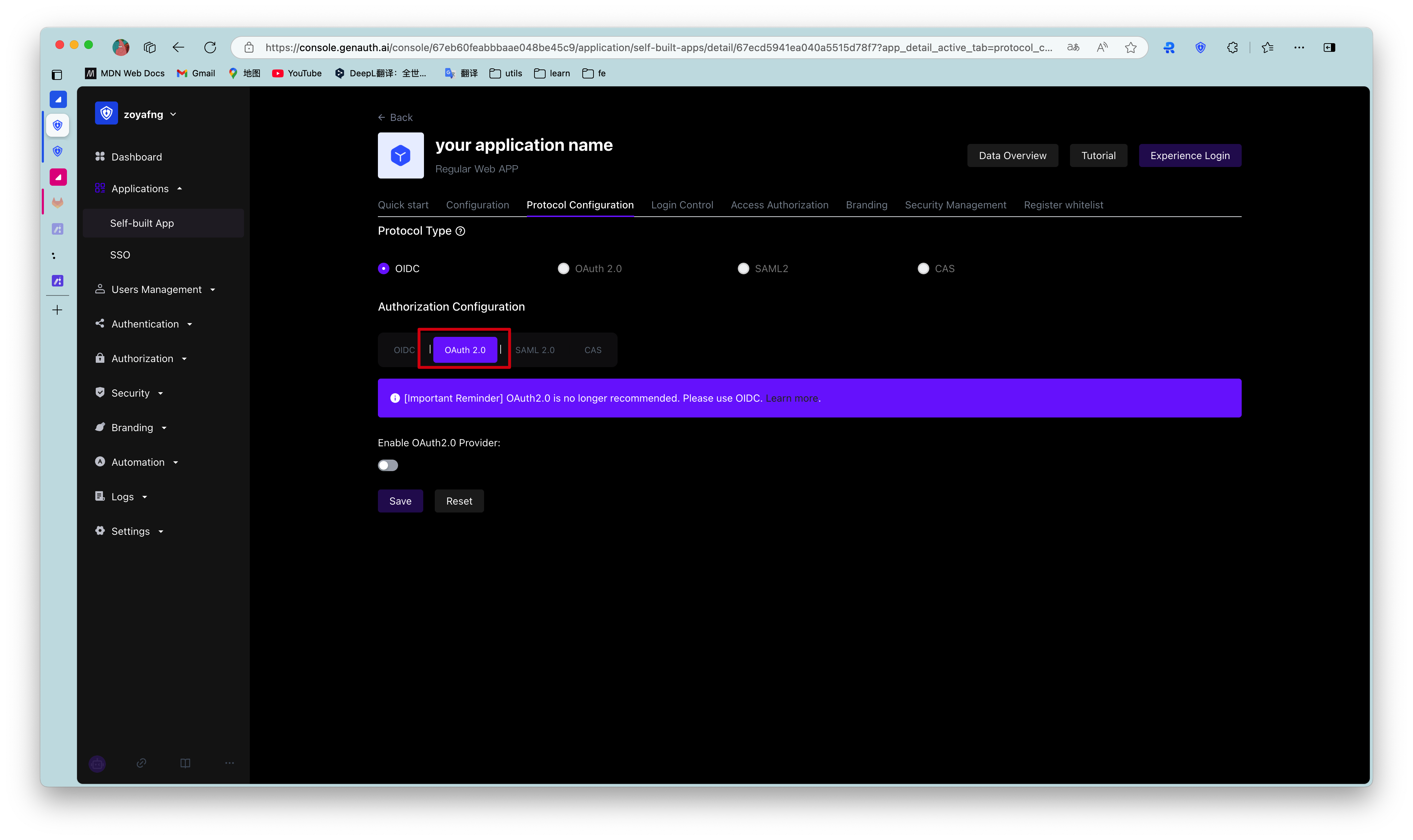
In the "OAuth2.0 Identity Provider" card below, turn on the Enable OAuth2.0 Provider switch and click Save.
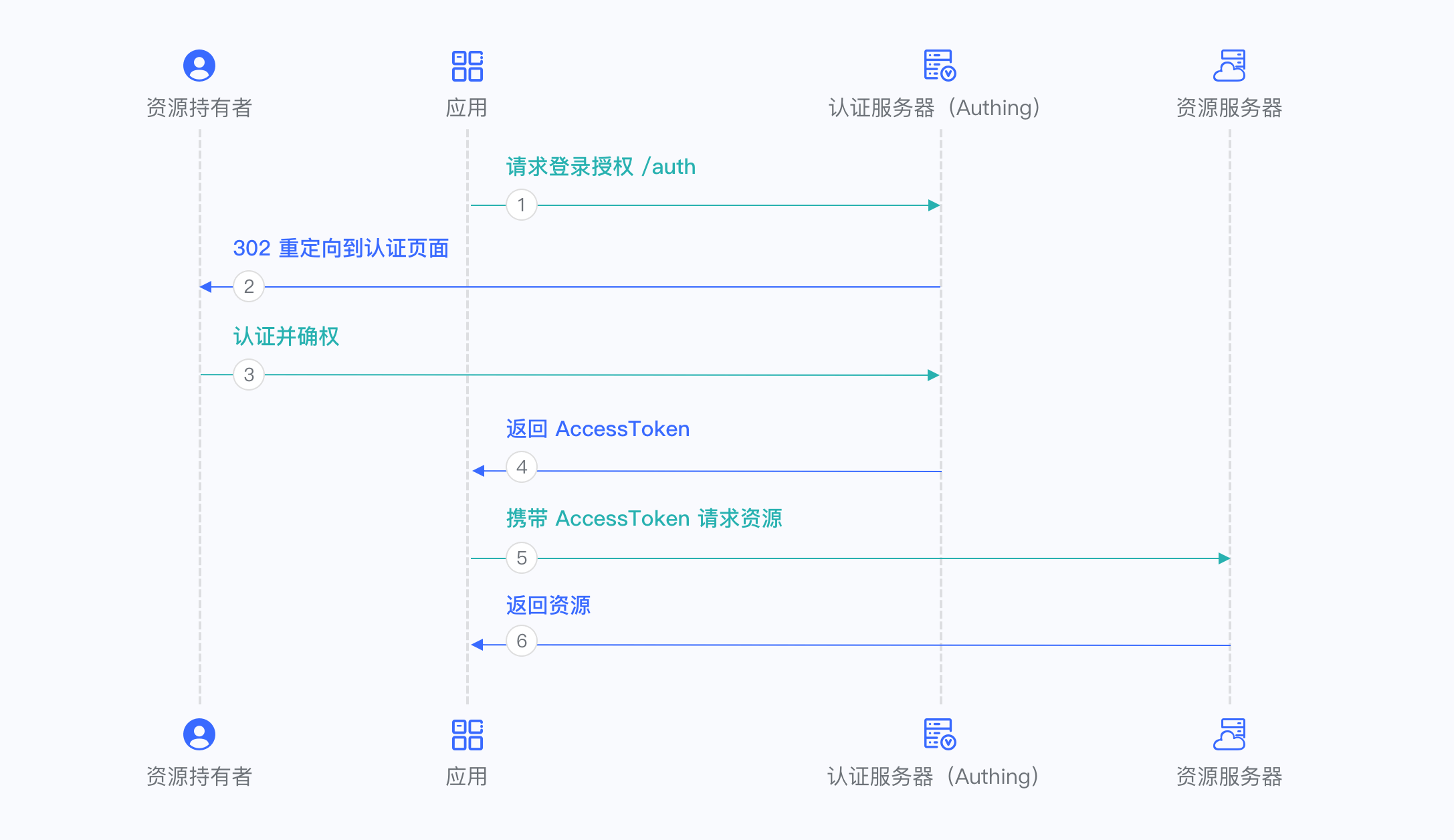
¶ Authorization Code Mode
If your application project has a backend service that can store keys securely, it is recommended to use the Authorization Code Mode.
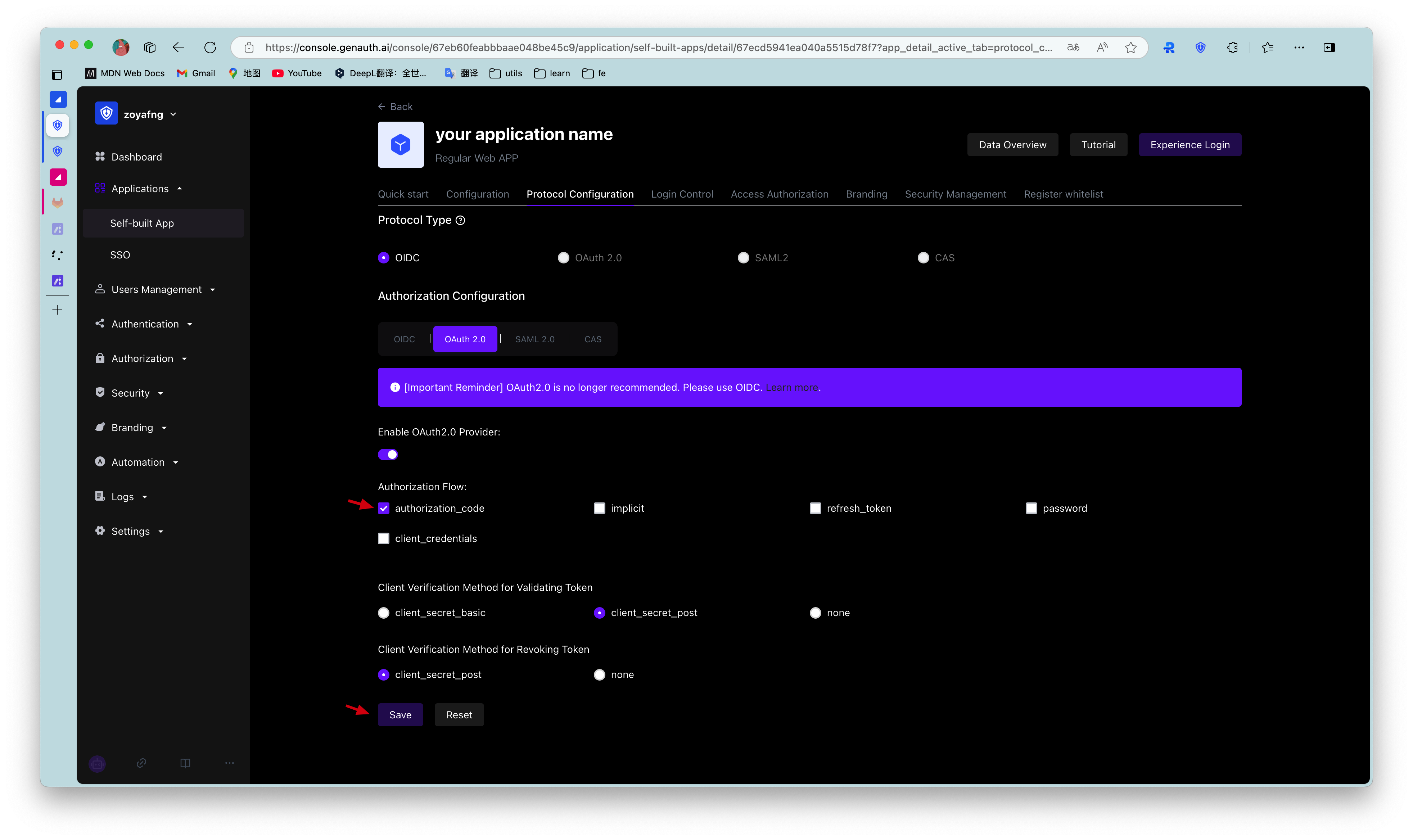
First, in Console > Application, find your application, enter the application details, enter the "Enable Identity Provider" tab, in the "OAuth2.0 Identity Provider" card below, check the authorization mode authorization_code, and then click Save.
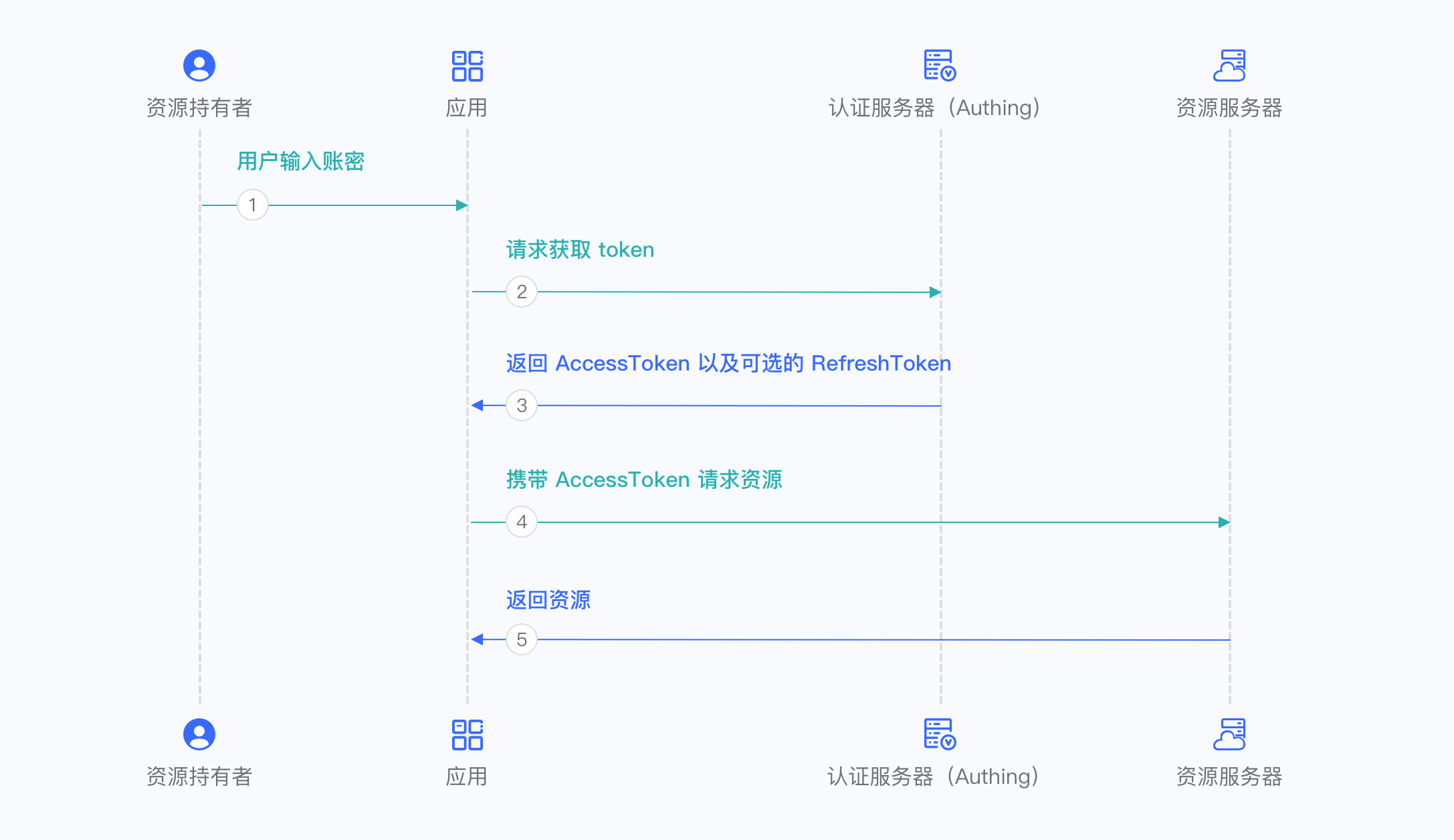
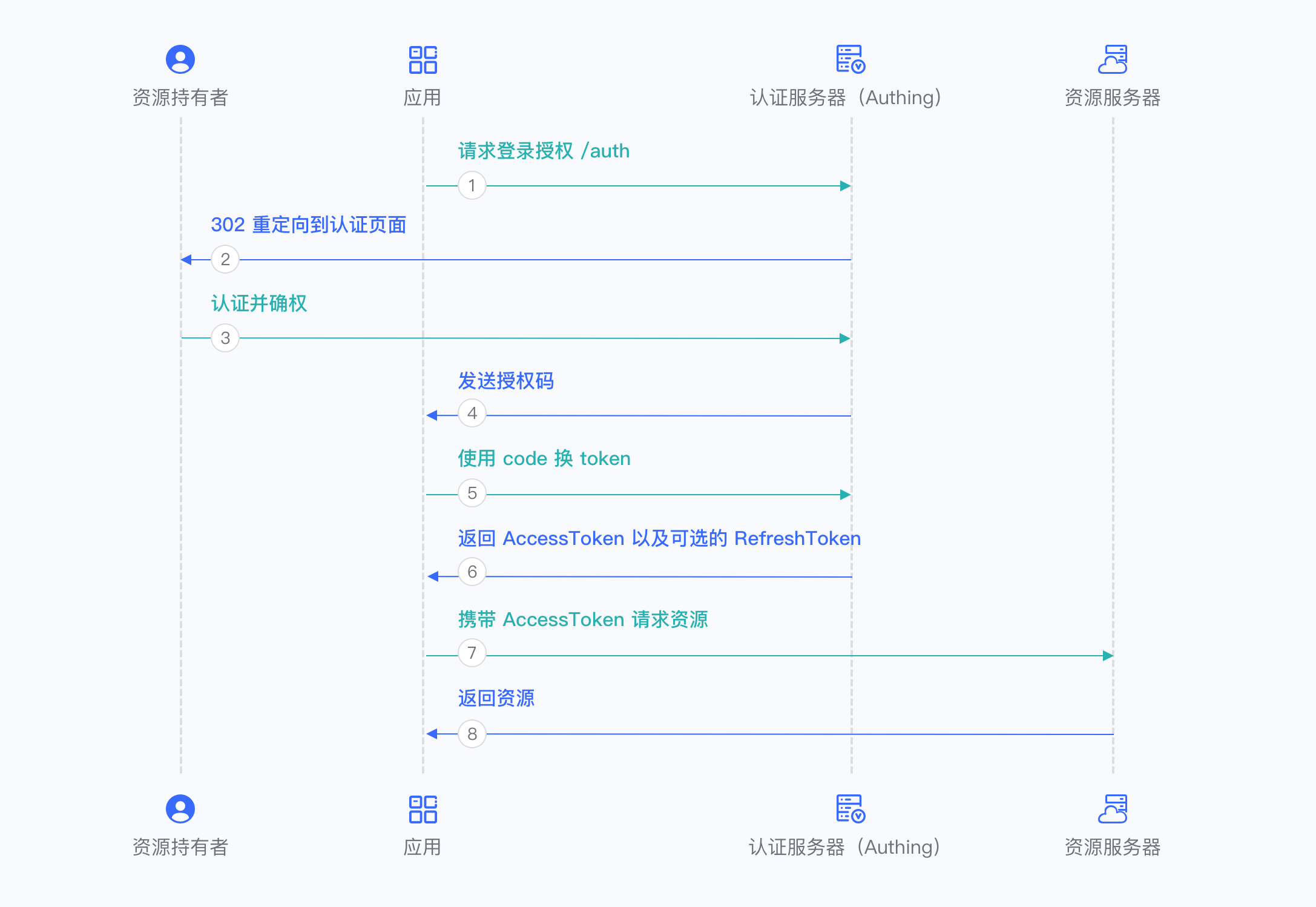
Overall, there is the following process.
- In your application, let the user visit the login link, the browser jumps to GenAuth, and the user completes authentication in GenAuth.
- The browser receives an authorization code sent from the GenAuth server.
- The browser sends the authorization code to your application backend through redirection.
- Your application service sends the authorization code to GenAuth to obtain AccessToken, and returns a refresh token if necessary.
- Your application backend now knows the user's identity, and can subsequently save user information, redirect to other front-end pages, use AccessToken to call other APIs of the resource party, and so on.
The flow chart is as follows:
¶ Implicit mode
If your application is a SPA front-end application and does not have a back-end service, it is recommended to use implicit mode to complete user authentication and authorization. Implicit mode is suitable for scenarios where keys cannot be stored securely (such as front-end browsers). In implicit mode, applications do not need to exchange codes for tokens, and do not need to request the /token endpoint. AccessToken will be returned directly from the authentication endpoint.
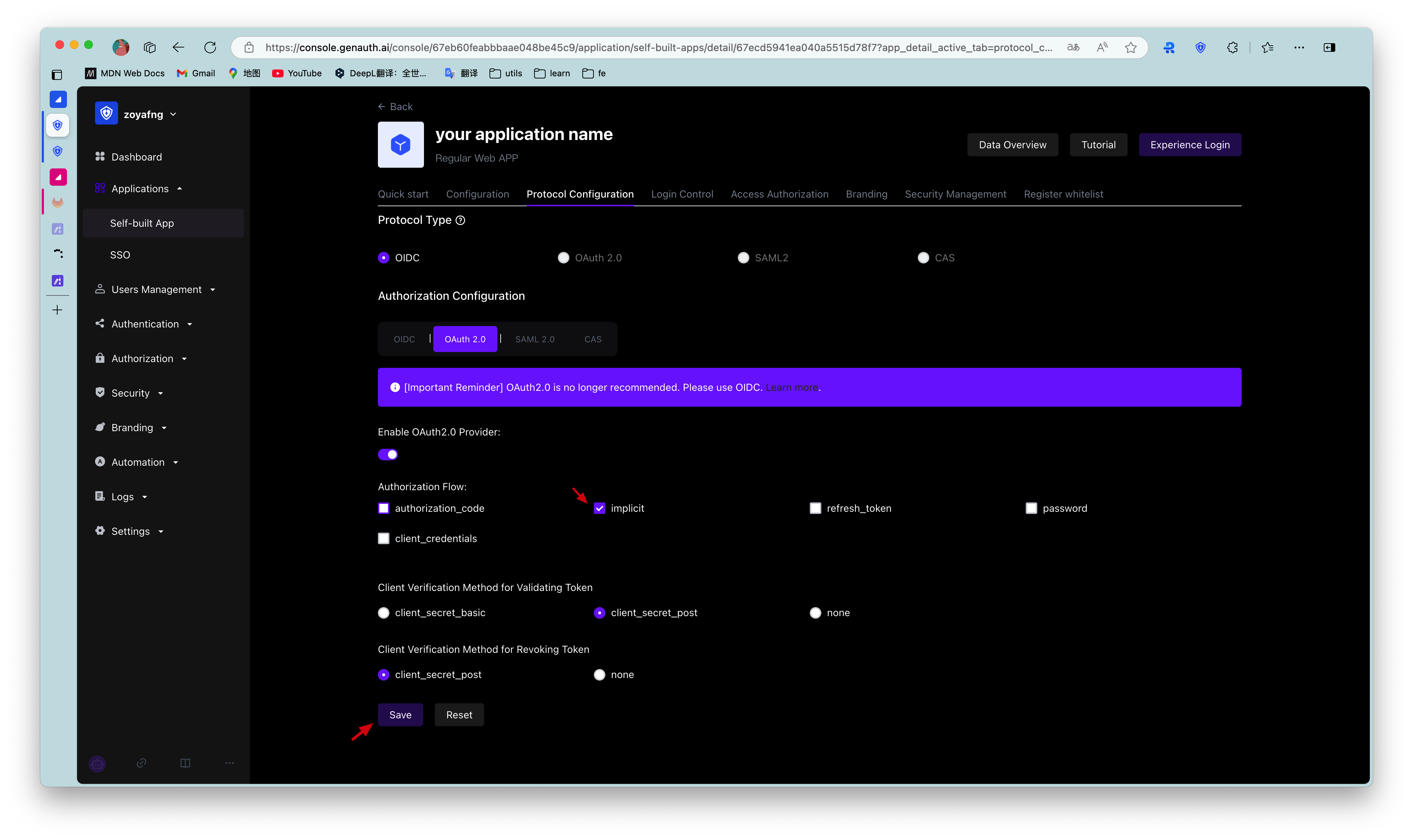
First, in the console > Applications, find your application, enter the application details, enter the "Enable Identity Provider" tab, and in the "OAuth2.0 Identity Provider" card below, check the authorization mode "implicit", and then click Save.
Overall, there is the following process.
- In your application, let the user visit the login link, the browser jumps to GenAuth, and the user completes the authentication in GenAuth.
- GenAuth redirects the browser to your application callback address, and the AccessToken is passed as the URL hash.
- Your application extracts the token from the URL.
- Your application can save AccessToken for subsequent use, such as using AccessToken to obtain user information and accessing resource servers with AccessToken.
The flow chart is as follows:
¶ Password mode
This mode is not recommended. Try to use other modes. Only when other modes cannot solve the problem will you consider using password mode. If you use password mode, please make sure that your application code logic is very secure and will not be attacked by hackers, otherwise it will directly leak the user's account and password. It is generally used to transform and integrate very old applications, otherwise never make it your first choice.
First, in Console > Application, find your application, enter the application details, enter the "Enable Identity Provider" tab, and in the "OAuth2.0 Identity Provider" card below, check password for the authorization mode, and then click Save.
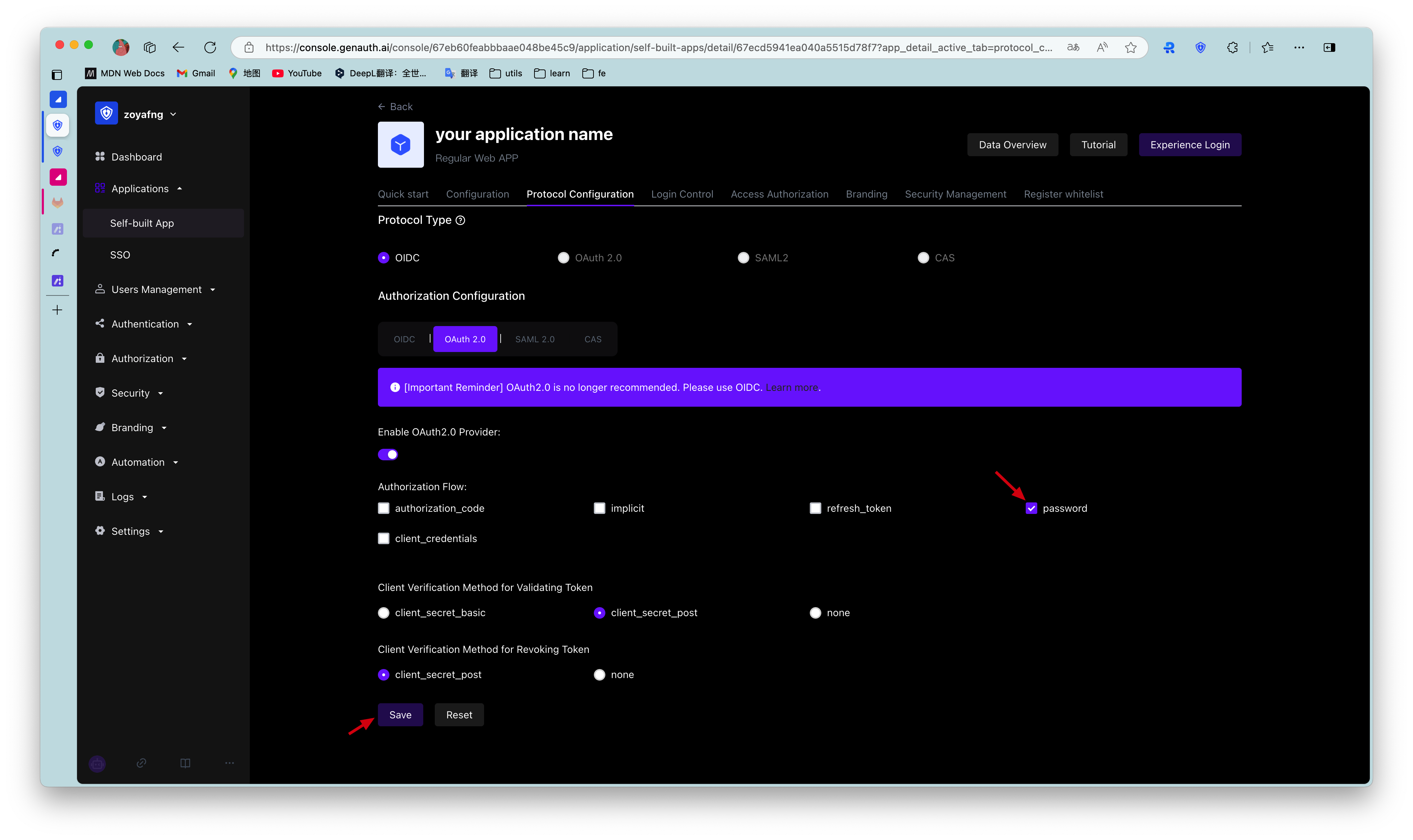
Overall, there is the following process.
- Your application asks the user to enter the account and password information.
- Your application sends the user's account and password to GenAuth.
- If the account and password are correct, GenAuth returns a token.
The flow chart is as follows: